Category: Artificial Intelligence
-
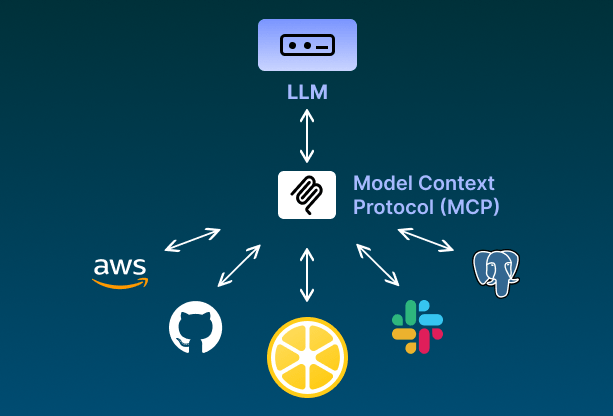
⚙️ The integration between LLM agents and DevOps tools is no longer science fiction.
MCP (Model Context Protocol) servers enable natural language agents to interact directly with key infrastructure, automation, and monitoring tools.This unlocks smarter workflows—where AI not only suggests… it acts.💡 Here are some MCP servers you can already use today:🔷 AWS MCP: control Amazon Web Services from an agent → https://github.com/awslabs/mcp 💬 Slack MCP: automate communication, channels,…
-

🧠 LangChain releases a powerful open-source AI agent builder
LangChain has unveiled its new open-source AI agent builder, a tool that allows developers to create, customize, and run intelligent agents directly in local environments—without relying on closed platforms or cloud services. This YAML-based framework enables step-by-step agent design, integration with tools like browsers, APIs, or execution environments, and testing with real-world examples. While accessible…
-

🚀 Xiaomi dives headfirst into the artificial intelligence race with MiMo, its own open-source language model.
MiMo 7B is Xiaomi’s newly launched language model, with 7 billion parameters, designed to directly compete with major players like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude. What stands out is its focus on logical and mathematical reasoning, where it has already outperformed larger models in key benchmarks. 📊 This model is not just an experiment. Xiaomi plans…
-

🤖 Amazon launches Nova Premier: its most advanced artificial intelligence model
Amazon has officially introduced Nova Premier, the most powerful artificial intelligence model in its Nova family. Designed to tackle complex tasks, it stands out for its multimodal capability, allowing it to process text, images, and videos with deep and contextual understanding. One of the most remarkable features of this model is its ability to handle…
-

🤖 Meta AI goes independent: now available as a standalone app with advanced voice capabilities
Meta has officially launched its artificial intelligence assistant, Meta AI, as a standalone application. This new app, powered by the Llama 4 language model, offers a more personalized and conversational experience, standing out for its advanced voice interaction and innovative social features. Key features include: 🗣️ Real-time voice interaction : Thanks to duplex voice technology,…
-

Alibaba launches Qwen 3: a new benchmark in open-source artificial intelligence 🤖🌍
Alibaba has announced the release of Qwen 3, an ambitious and advanced family of AI models ranging from lightweight versions to a Mixture of Experts (MoE) model with 235 billion parameters. This development is available under an Apache 2.0 license, reinforcing the company’s commitment to open and collaborative innovation. Qwen 3 stands out for its…
-

OpenAI O3 and O4: A leap towards autonomous and multimodal AI
OpenAI has unveiled its new O3 and O4 models, marking a significant breakthrough in the field of artificial intelligence. These models combine text and image processing capabilities, allowing for more accurate reasoning and more natural responses. The ability to understand visual content and use it in reasoning represents a substantial improvement over previous versions. According…
-
Google launches Agent2Agent
The protocol that connects AI agents. Google introduced Agent2Agent (A2A), an open protocol designed for artificial intelligence (AI) agents to exchange information and coordinate actions, even if they were developed by different companies or technologies. Unlike traditional automation systems, these agents are able to dynamically adapt and make decisions autonomously. With A2A, they operate under…
-

MCP on GitHub
A New Way to Integrate AI into Development The Model Context Protocol (MCP) server on GitHub is an innovative tool that allows developers to improve their workflow by integrating artificial intelligence. This standardized protocol makes it easy to automate tasks, efficiently manage repositories, and incorporate advanced features directly into the development environment. MCP is designed…
-

🚀 Google Launches the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
The Agent Development Kit is an open-source toolkit designed to simplify the creation of artificial intelligence agents. It also offers a catalog of ready-to-use agents on its cloud computing platform. With this initiative, Google promises that developers will be able to build an AI agent in under 100 lines of code, orchestrate agent systems, and…